Drip Irrigation:
Today, we are learning the Drip Irrigation system.
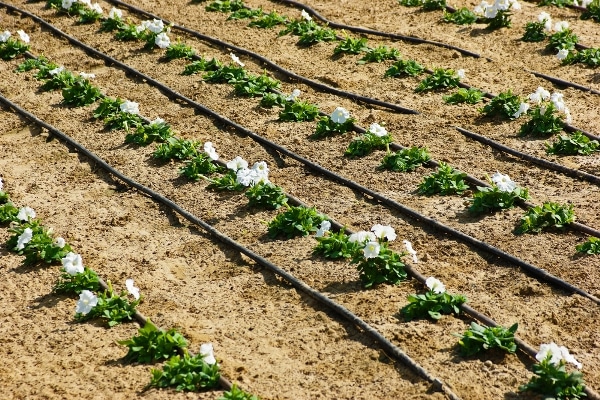

Introduction to Drip Irrigation:
What is drip irrigation? Well, drip irrigation is a form of irrigation that saves water and makes use of manure/fertilizer efficiently by allowing water to draw slowly to the roots of plants/trees, either onto the soil surface or directly onto the root area of the plant. The drip irrigation works through a network of valves, pipes, tubing, and emitters. It is done through narrow tubes that deliver water directly to the base of the plant/tree. The drip irrigation system may also use devices called “micro-spray heads”. This device sprays water in a small area of the field instead of dripping the water from emitters. Generally, this type of spray heads is used on tree and vine crops with wider root zones.
In the case of less water available or recycled water utilization, sub-surface drip irrigation (SDI) uses permanently or temporarily buried dripper line or drip tape located at or below the plant roots. In order to find out a suitable drip irrigation system to be installed, One should consider factors like land topography, soil, water, crop, and agro-climatic conditions. The drip system can be used in most of the farming methods like commercial greenhouse farming, residential gardens, polyhouse farming, shade net farming, hydroponics, and open field farming. Drip irrigation will be more beneficial when compared to the sprinkler irrigation system. Drip and subsurface drip irrigation is used when using wastewater. Generally, large drip irrigation system consists of some kind of filters to prevent clogging of the small emitter flow path by small waterborne particles. Nowadays, one can get drip systems which minimize the clogging. Currently, drip irrigation for the home garden is available in the form of drip kits and these are getting popular for the homeowners. This kit consists of a timer, hose, and emitter.
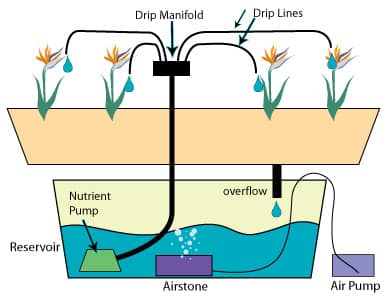
Main Components involved in Drip Irrigation:
The following components are used as part of the drip irrigation system.
- Pump
- Filtration systems like a water filter, sand filter (separator), Fertigation systems (mixing liquid fertilizer with the irrigation water is called “Fertigation”).
- Pressure Controller (Like Pressure Control valve/regulator).
- Backwater flow prevention unit.
- Large Pipe and Pipe fittings (Mainline Pipes).
- Hydraulic control valves and safety valves.
- Smaller diameter poly-tube which is referred to as “laterals”.
- Poly fittings and accessories to make drip connections.
- Emitters or drippers, micro spray head, in-line dripper or in-line drip tube.
Note: In the drip system, pump and valves may be operated manually or automatically.
Advantages of Drip Irrigation:
The following are the advantages of a drip irrigation system.
- Useful in areas where water availability is a major problem.
- Increase in yield and early maturity of the crop can be expected.
- Reduces Fertilizer/Nutrient loss due to localized application.
- Makes use of water in a highly efficient way.
- Drip irrigation makes intercultural operations easy.
- Water distribution is done uniformly and directly to the plant root zone.
- Controls weed growth and soil erosion.
- Land/fields with irregular shapes can utilize drip system very effectively.
- Recycled wastewater can be used without any issue.
- Can save the labor cost when compared to other irrigation methods.
- Reduces the risk of plant and soil-borne diseases.
- It can be operated at a lower pressure which may reduce energy consumption cost.
- There is no need for levelling the land to be cultivated.
- Because of the uniform distribution of water, the plant root zone can be maintained with constant moisture capacity.
- Fertigation (Pumping the fertilizer along with irrigated water through drip system) can be done with minimal waste of fertilizers/micro-nutrients.
- Water output variation can be controlled very easily by operating valves and drippers.
- Due to the drip system, soil type plays a minimal role in the frequency of irrigation.
- Ultimately, the drip system saves time and money.

Disadvantages of Drip irrigation:
The following disadvantages of the drip irrigation system.
- Cost of drip system can be more when compared to overhead systems. However, one can avail subsidies provided by local government schemes.
- The drip system cannot be used for frost control, unlike the sprinkler system.
- The drip tube system can have a shorter life as they are exposed to sunlight.
- Without proper/sufficient leaching, salts applied with the irrigation water through drip may build up in the root zone of the plant.
- If the filtration is not done properly, it can result in clogging.
- If herbicides or top dressed fertilizers need sprinkler irrigation, drip system may not fit into the situation.
- The PVC pipes may require replacement of the entire tube and can result in increased maintenance cost.
- Extreme care is needed while setting up a drip irrigation system such as proper design, installation, and quality material.
- Drip tape causes extra clean-up tasks frequently which can result in an increase in maintenance cost.
Drip Irrigation Vs Sprinkler Irrigation:
Drip irrigation is more beneficial when compared to drip irrigation. The following are the main disadvantages of the sprinkler system.
- Sprinkler system results in uneven water application from wind and extreme temperatures.
- There may be water loss from evaporation during irrigation through sprinklers.
- Sprinkler system causes wetting of foliage (collection of plant leaves). This leads to increased risk of disease and fungi growth.
- Improperly maintained sprinkler spray angles near buildings and walkways can damage fixtures.
Cost of Drip irrigation:
Cost of drip irrigation depends on the region/area. Here we are providing a rough (ballpark) estimate which will cover from low to high range. However, they may change time to time because of market conditions. Some countries like India is providing up to 90% of subsidy for small farmers who are holding less than 5 acres of land. Contact your agriculture department for subsidy information.
| Item Details | Quantity | Low | High |
| Drip Irrigation System Cost Non-discounted retail pricing for PVC connector piping/tubing, drip elements, solenoid operated zone valves, and timer. Quantity includes typical waste overage, material for repair and local delivery. |
125 square feet |
$53
|
$80 |
| Drip Irrigation System Labor Cost Labor estimate to install a drip irrigation system. Connect pressure regulator to the power supply. Route main tubing. Install drip lines with drip or spray fitting at 1m/3 feet intervals. This Includes planning, equipment and material acquisition, area preparation and protection, set-up and clean-up. |
4 hours | $105 | $260 |
| Drip Irrigation System Materials and Supplies Cost Cost of connectors, fittings, adhesives and fabrication solvents. |
125 square feet | $10 | $30 |
| Total Cost to Install Drip Irrigation System for 125 square feet | $178 | $370 | |
| Average Cost Per Square Foot of Drip System | $1.424 | $2.96 |
Cost of Drip irrigation for Indian Farmers:
Generally, drip Irrigation provides the facility to irrigate the plants at the root zone through emitters fitted on a network of pipes. The emitting devices could be drippers, microjets, misters, fan jets, micro sprinklers, mini sprinklers, micro sprayers, foggers, and emitting pipes, which are designed to discharge water at prescribed rates. Basically, the use of emitters depends on specific requirements that may vary for each crop. Generally, the factors that decide the choice of the emitting system are; water requirement, the age of the plant, spacing, soil type, water quality. Sometimes micro-tubes are also used as an emitter, though it is inefficient. All types of surface and subsurface irrigation systems are covered under micro-irrigation. An indicative list of system components required for installing a drip irrigation system in areas ranging from 0.4 ha to 5 hectares is given in below table. The estimated cost of the drip irrigation system in India is given in Indian Rupees here.
Area in Hectares
Spacing in meters
0.4
1
2
3
4
5
12mx12m
10,700
16,800
25,400
32,700
53,900
71,500
10mx10m
12,200
18,200
27,900
36,100
58,200
77,100
9mx9m
12,500
22,300
35,700
56,000
61,700
81,300
8mx8m
13,000
20,100
31,400
41,700
65,700
86,300
6mx6m
14,400
30,300
51,300
70,300
1,05,900
1,37,500
5mx5m
15,100
32,900
56,700
83,100
1,17,300
1,50,800
4mx4m
16,900
39,400
63,200
1,00,700
1,42,400
1,79,400
3mx3m
17,900
35,700
71,400
96,100
1,30,900
1,58,400
3mx1.5m
19,700
40,100
80,500
1,09,700
1,46,300
1,80,900
2.5mx2.5m
20,000
39,900
81,400
1,11,200
1,99,700
2,39,600
2mx2m
21,400
49,900
86,400
1,22,700
1,65,000
2,23,400
1.5mx1.5m
26,100
55,000
10,9500
1,65,100
2,06,000
2,81,000
1mx1m
26,500
57,600
96,500
1,46,500
2,00,000
2,49,300
 Basically, the unit cost of Drip Irrigation system depends on plant spacing and location of the water source. Another fact is that the cost of the drip system differs from each state. Accordingly, the States have been categorized into three categories, like Category “A”, “B” and “C”. States in India where more than 10,000 hectares have been brought under drip irrigation as on 1.4.2004 would come under ‘A’ Category. This would include the States of Andhra Pradesh (AP), Telangana, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu. All the States except those covered under Category ‘A’ and those falling in the Himalayan belt comes under Category ‘B’. All the North Eastern States, Sikkim, Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), Uttaranchal, HP (Himachal Pradesh), and Darjeeling district of West Bengal comes under Category ‘C’. the cost of drip system in Category ‘B’ States is estimated to be 15 to 16% higher than Category ‘A’ States while for Category ‘C’ States it is estimated to be 25 to 26% higher than Category ‘A’ States. Accordingly, the average unit cost of drip irrigation system for different state categories in India is provided below.
Basically, the unit cost of Drip Irrigation system depends on plant spacing and location of the water source. Another fact is that the cost of the drip system differs from each state. Accordingly, the States have been categorized into three categories, like Category “A”, “B” and “C”. States in India where more than 10,000 hectares have been brought under drip irrigation as on 1.4.2004 would come under ‘A’ Category. This would include the States of Andhra Pradesh (AP), Telangana, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu. All the States except those covered under Category ‘A’ and those falling in the Himalayan belt comes under Category ‘B’. All the North Eastern States, Sikkim, Jammu and Kashmir (J&K), Uttaranchal, HP (Himachal Pradesh), and Darjeeling district of West Bengal comes under Category ‘C’. the cost of drip system in Category ‘B’ States is estimated to be 15 to 16% higher than Category ‘A’ States while for Category ‘C’ States it is estimated to be 25 to 26% higher than Category ‘A’ States. Accordingly, the average unit cost of drip irrigation system for different state categories in India is provided below.
Using Drip Irrigation in Greenhouse -Polyhouse.
|
State Category |
Average Cost, Indian Rupees/ha |
| A | 40, 000 |
| B | 46,000 to 47,0, 0 |
| C | 50,000 to 5100 |
Subsidy on Drip irrigation:
The following subsidy information is applicable to Indian farmers/growers. However, you can contact your local horticulture/agriculture departments for current subsidy information on an agriculture drip system.
Centrally Sponsored Schemes and State government schemes are available for drip system subsidy in India. This subsidy varies from state to state and extent of the land owned by the farmer.
- Farmers with holding up to 2.5 acres of dry land or 1.5 acres of wetland are defined as Marginal Farmers & eligible up to 90% of subsidy. However, it varies from state to state, contact your local horticulture/agriculture department.
- Farmers with holding up to 5 acres of dry land or up to 2.5 acres of wetland are defined as Small Farmers & eligible up to 90% of subsidy. However, it varies from state to state; contact your local horticulture/agriculture department.
- Farmers with land holding above 5 acres of dry land or above 2.5 acres of wetland are defined as Other Farmers & eligible up to 60 to 80% subsidy. However, it varies from state to state; contact your local horticulture/agriculture department.
The following criteria should explain about Farmer’s eligibility.
- 16% of the total financial target shall be covered by schedule caste farmers.
- 55% of the total financial target shall be covered by schedule Tribes farmers.
- Not less than 25% of the total financial target shall be covered by BC farmers.
- Not less than 50% of the total financial target shall be covered by SF/MF farmers;
- Not exceeding 10% of the financial target shall be covered by other farmers (more than 5 acres of land holding).
- Generally, preference is given to Small and Marginal Farmers, SC/ST/BC/Women and differentially abides (PH) farmers.
Note: The above-given information may not be accurate but a rough estimate, Please contact local horticulture/agriculture technical department for current schemes/subsidies/loans and other information.
Bottom line:
Properly designed, installed, and managed, the drip irrigation system helps in achieving water conservation and efficiently using fertilizers/manures.

Hi, I am in the process of developing an Agriculture and Poultry farming, I would like to receive information and help. Thanks
Please, I would like to receive the information for agriculture and poultry farming.