Maize Cultivation Guide:
Introduction of Maize Cultivation and Importance:- Maize is popularly known as “Corn” and is one of the most versatile emerging cereal cash crops having wider adaptability under variety of climatic conditions. The word “maize” derives from the Spanish form of the indigenous Taino word for the plant, maiz. It is called queen of cereals globally. In Asia, maize is the third most important food cash crops after wheat & rice. The maize can be grown throughout the year in most of the Asian countries for various purposes including fodder for animals, food grain, sweet corn, baby corn, green cobs, and pop corn. Corn flour is being used in food preparation of various Asian dishes. Corn is consumed widely in Indian cooking. There are many other uses of maize and this serves as a basic raw material to thousands of industrial products that may include oil, starch, alcoholic beverages, alcoholic beverages, pharmaceutical, food sweeteners, food cereals, cosmetic, and film, gum, textile, package and paper industries. Maize production also contributes good value to Asian economy. commercial farming of maize is quite successful due to its wider adaptability under variety of climatic conditions low investment.
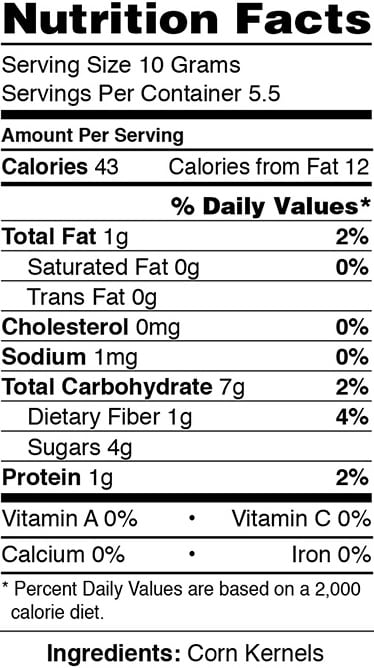
Health Benefits of Corn:- Below given are some of the health benefits of corn.

- Corn is good for digestion due to its fiber content.
- Corn helps in lowering bad cholesterol (LDL).
- Corn is good for heart health.
- Corn helps in preventing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Corn prevents diabetes & hypertension.
- Corn has anti cancer properties.
- Corn helps improving vision.
- Corn may prevent skin problems.
- Corn may combat with hair loss.
Major Maize Production Countries:- The following are the top 10 production countries of maize/corn in the world.
Major Con Producers of India:- In North India, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir and Punjab which together account for two-third of the total area and output of the maize crop. Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana are the major production states of maize in south India. Madhya Pradesh tops in production of corn in the country.
Commercial Varieties of Maize:- There Number of hybrid commercial improved maize varieties available from the seed companies. Selecting right cultivar plays major role in getting good yields. Some of the commercial hybrid varieties in India are: Himalayan 123,30V92,30B07, Sona, Kisan,30R77,Hi-Starch, 31T15, 32T25,Ganga-1, Ganga-101,Deccan, Ganga-5, Ganga-Safed-2, Ganga-4, Ganga-3 and V.L. 54, Vijay, Amber, Jawahar, Vikram and Ranjit. In other Asian regions, consult local agriculture department or university for recommended local cultivars.

Local Names of Maize in Asia:- Ogsusu (Korean), Maka (Hindi, India), Makai (Nepali), Mais (Filipino), Dhúra (Arabic), Makai (Urdu), 玉米 (Chinise), ข้าวโพด (Thai), bắp(Vietnamese), ඉරිඟු (Sinnhalese, Sri Lanka), メイズ, tōmorokoshi (Japanese), Misir (Turkish), Jagung (Malay), balâl (Persian), эрдэнэ шиш (Mangolian), 玉蜀黍 (Taiwanese).
Local Names of Maize in India:- Maka (Hindi, Marathi, Oriya), Moko (Konkani), Bhutta (Bengali), Makki (Punjabi), Makai (Gujarati), Mokka Jonnalu (Telugu), Makka Cholam (Tamil), Cholam (Malayalam), Chujak(Manipuri), Makaa’y (Kashmiri), Musikinu jola (Kannada).
Climatic requirements for Maize Cultivation:- In Asian countries, maize is primarily a rain fed crop which is sown just before monsoon rains . This maize crop usually thrives best under temperatures varying from 21°C-30°C, although it can tolerate temperatures as high as 35°C.This crop is effected by frost, so it is grown where at least 5 frost free months available in a year. It requires at least 50 to 100 mm of rainfall. It is not recommended to cultivate this crop in the areas where rainfall is more than 100 mm.

Sowing Season for Maize Cultivation:- Maize crop is usually grown in Asia during June to July, September to October and Jan to Feb seasons. For maize seed production, sowing during Nov to Dec is suitable since seed maturity will not coincide with rainy season.
Land Selection and Field Preparation in Maize Cultivation:- The selected field should be free of volunteer maize plants. What are volunteer plants?: volunteer plants are basically unwanted plants that are grown from previous maize crop. These maize plants may be different variety, so there is chance that genetic contamination may occur. Ploughing should be done to get fine tilth stage of soil and make the field weed free. It may take 5 or 7 ploughings to bring the soil to friable stage. At least 15 to 20 tons of well decomposed farm yard manure (FMY)/ha should be applied across the field or composted coir pith and apply 10 Azospirillum packets in the field. Prepare furrows and ridges with 45 cm to 50 cm spacing to save the irrigated water.
Seed Rate and Seed Treatment in Maize Cultivation:- 11 to 12 kg of maize seed is required for sowing one hectare land. To control seed borne pathogens of downy mildew (fungal disease), should treat seeds with thiram or carbendazim @ 2 grams per kg of seeds. One day after seed treatment, should treat the seeds with 600 grams of Azospirillum with rice gruel and shade dry for 15 to 25 minutes. Azosprillum help in fixing the atmospheric nitrogen in the soil.

Sowing method in Maize Cultivation:- In Maize Cultivation, propagation is done through seeds. It is recommended to adopt a plant-to-plant spacing of 10 cm and sow 2 seeds per hill. Should sow the seeds @ 1/3 rd of ridge from the bottom.

Manures and Fertilizers in Maize Cultivation:- Among all the cereals, maize in general and hybrids in particular are responsive to nutrients applied either through organic or inorganic sources. The rate of nutrient application depends mainly on soil nutrient status/balance and cropping system. For obtaining desirable yields, the doses of applied nutrients should be matched with the soil supplying capacity and plant demand by keeping in view of the preceding crop. Other than Farm Yard Manure applied at the time of land preparation, should apply inorganic fertilizers like 475 kg of super phosphate, 200 kg of urea, and 180 kg of potash per ha as basal dose. 20 days after sowing, should apply 50 to 60 kg of urea and at 45 days after sowing 120 kg of urea and 50 kg of potash as top dressing.
Micro nutrient deficiency in Maize Cultivation:- Nutrient deficiency in maize affects the growth of the plant, so the yield. Zinc and Magnesium deficiency are very common and largely occurs in leaves. To deal with these deficiencies, make sure to apply ZnSO4 @ 20 to 22 kg per hectare as basal fertilizer. Magnesium deficiency will cause yellowish symptoms between edges and veins of basal leaves. Due to “Fe” or “Iron” deficiency, the whole plant will turn into yellowish colour, to correct these deficiencies, supplement the micro nutrient mixture at 63 per hectare mixed with 45 kg of sand, after sowing the maize seeds in the field.

Irrigation in Maize Cultivation:- Provide immediate irrigation after sowing is done in the field. Subsequent life irrigation should be given on 3rd or 4th day and based on the soil type and season. (It may no bet required in rainy season). Usually in maize cultivation, during initial to 3 to 4 weeks, less number of irrigation are recommended. Subsequent irrigations should be given once in a week. During early stage of this crop, water lagging should be avoided and should have good drainage in the soil.

Weed Control/Inter Culture Operations in Maize Cultivation:- It requires at least 2 to 3 hand weeding in maize crop, one is at 3 weeks time and another is in 40 to 45 days after sowing the crop. Apply fertilizers as top dressing and do the earthling up operation after weeding is completed. Spray Atrazin 500 grams mixed in 1000 liters of water and life irrigation on thirds or fourth day will check the weeds in maize crop field.
Diseases and Insects in Maize Cultivation:- The main diseases found in Maize cultivation are downy mildew and leaf spot.
- Downy mildew: In order to control this, remove the affected plants. Spray Metalaxyl 72 WP @ 1 kg per hectare, or Mancozeb 1 kg per hectare, 21 days after sowing.
- Leaf spot: To control this, spray Captan or Mancozeb kg per hectare when the disease intensity is high. Usually, insect attacks are very low in corn crop. In young plants, only shoot fly affects and stem borer affects the shoot after 21 to 30 days after sowing. As part of control measures, apply carbofuran granules @ 8 kg/acre @ 2 granules/ each plant.
Harvesting of Maize or Corn:- Harvesting should be done when the crop outer cover of the cob turns from green to white colour. Harvesting can be done by hand. Machines can be used to separate the seeds from the cob.

Yield of Maize or Corn:- Maize yield depends on various factors like the cultivar selected, soil type, farm management practices, methods followed and climatic conditions. With good filed management practices and good seed variety yield of 2500 kg per hectare can be obtained.

Marketing in Maize Cultivation:- Can transport to local markets or nearest corn processing mills.
Bottom Line in Maize Cultivation:- Farmers can get good profits in short period (4 months) of time with low investment.
For Indian Agriculture Guide: Read here.
For Sheep or Goat Farming Guide: Read here.
