Growing Grapes Organically – A Beginners Guide
Hello friends this article would give you an insight into the organic cultivation of grapes in vineyards.
Introduction
Grapes are one of the most priced horticulture commodities in the Asian agriculture industry. The two cultivated species of grapes in Asia are Vitis viniferae and Vitis amurensis of which the former species is highly used for commercial cultivation. The economic importance of grapes is possibly due to their versatile nature to obtain a variety of value-added and processed products which include raisins, wine, candy, and vinegar. China, Turkey, and India top the list of grape production in Asia. While countries like Pakistan, Japan, Myanmar, and Thailand also cultivate grapes for commercial purposes.
A step-by-step Planting Guide to Growing Grapes Organically

Cultivars for Growing Grapes Organically
Grapes offer extensive varieties of cultivar, which can be classified based on the purpose of growing, the colour of the fruits and the presence of seed. Some important cultivars with the purpose of growing are enlisted below:
- Winemaking
- The cultivars suitable for red wine are Cabernet Sauvignon, Cabernet Franc, Merlot, French blue, Muscat Hamburg, Pinotage, Syrah, and Bangalore Blue.
- The cultivars suitable for white wine are Chardonnay, Italian Riesling, Ugni Blanc, Chenin Blanc, Gewurztraminer, Sauvignon Blanc, Semillon, White Riesling and Rkatsiteli
- Raisins – Merbein Seedless, 2A-Clone, Manjari Kishmish and Thompson Seedless
- Table Purpose –
- White-Green grapes – Thompson Seedless, Perlette, Early White, Rosario Bianco and Goldfinger.
- Red grapes – Flame Seedless, Crimson Seedless, Red Globe, Kings Ruby and Ruby Roman
- Blue-Black grapes – Purple Seedless, Fantasy Seedless, Manjari Shyama, Sharad Seedless and Nanasaheb
Soil Requirements for growing Grapes Organically
Grapes can thrive almost in all types of soils ranging from sandy to clayey soil with a good drainage system. However, heavy clay soils must be avoided as they create the problem of waterlogging going. They are highly sensitive to saline and alkaline soil and don’t perform well in such conditions. The most suited pH range for grape cultivation lies between 5.5-7. Well, drained, deep loam soils enriched with organic matter works best for the establishment of the grape vineyard.
Climatic Requirement for growing Grapes Organically
Climatic requirement for grape cultivation varies from species to species. The hot and dry climate is ideal for Vitis viniferae. Climatic requirements are detrimental factors for fruit development and its harvest quality. Temperature plays a major role in the colour development of grapes. While high humidity and precipitation are conducive to disease incidence and unripe berries. The ideal sunshine hours for grape are in the range of 6-8 hours per day with an optimum temperature of 220C temperature during the growing season.
Planting Material for growing Grapes Organically
Hardwood stem cuttings are used for commercial propagation in grapes fruit. It can also be propagated through seeds, grafting and buddings. These cuttings are procured from October pruning in Indian Peninsula. The cutting must have at least 4 nodes with a diameter of 8-10mm. These cuttings may be grafted on rootstocks, Dogridge and Rootstock-1613 to overcome the problem of salinity and nematode prone soil respectively.
Planting Procedure of Grapes
The best time for planting rooted cutting is February-March while grafting must be done during October. The cuttings should be raised in the nursery to initiate rooting and then transplanted in the field. The spacing can be maintained at 2.5m×1.5m, 2.75m×1.5m, or 3.0m×1.5m. Considering 2.75m×1.5m as optimum plant spacing we require around 982 plant cuttings per acre area of cultivation.
Steps for the Establishment of Vineyard
In case if you miss this: Spirulina Farming Guide.

- Land preparation must be done one before the date of planting.
- Weeds like carrot grass and nutgrass must be completely removed from the area as they compete for space, nutrients, water, and light with the plant.
- Land must be levelled by a land leveller before going for trench making. The trench must be oriented in a North-South direction. The size of the trench should be 75cm deep and 75cm in width. The 2 trenches must be 2.5m-3m apart.
- The opened trench must be allowed to sun exposure for 10-15 days, before filling operation.
- The trench is filled up to 2 inches by topsoil followed by the addition of green manure crops like Sesbania bispinosa (Dhaincha), Crotalaria juncea (Sunn Hemp) and other nutrient amendments are as follows:-
- Farmyard Manure – 20 kg per foot of trench length
- Nutrient mixture – 500g SSP + 100g Urea + 100g SOP + 200g MgSO4 + 10g Micronutrient Mixture per foot of trench length
- Now the trench can be covered by bottom soil and levelled properly.
- Light furrows must be made in the covered trench after levelling to facilitate flood irrigation, which is to be followed immediately after trench covering.
- After 3-5 days of the flood, irrigation planting is done. Evening hours are preferable for planting as compared to a morning or peak hours to avoid heat shock to plants.
- For planting pits of 30cm*30cm*30cm dimensions are dug. The distance between the pits vary from 1.5m-2m depending on the soil type, for heavy soil it is 2m and for light soil, it is 1.5m.
- The pits are filled with 100g FYM and 500g sand. The plant should be kept in the centre of the pit and pressed with the soil firmly.
- In the case of plants in polythene bags, special care must be taken while removing it from the bag and avoiding any injury to the plant.
- If the rooted plants are taken from nursery beds green portion and leaf must be removed before planting.
- Planting is immediately followed by irrigation.
- Once the rootstock is planted, it takes 10-15 days to start its new growth.
Care of the Rootstock After Grape Planting
- Irrigation – Light irrigation of plants must be done on daily basis for 1 month after planting, after that irrigation can be done on alternate days for heavy soils and every day in light soil.
- Nutrient Management
| Manure and Fertilizer Applied to Young Rootstock Plant | ||
| Period After Planting (in Days) | Nutrient/Fertilizer formulation | Quantity (kg/acre/day) |
| 0-15 | – | – |
| 16-30 | Urea | 0.5 |
| 31-45 | NPK 19:19:19 | 1.0 |
| 46-60 | Urea | 0.5 |
| 61-75 | NPK 19:19:19 | 1.0 |
| 76-90 | Urea | 1.0 |
| 91-105 | NPK 19:19:19 | 1.0 |
| 106-120 | Urea | 1.0 |
| 121-150 | NPK 13:0:46 | 1.0 |
| 151-180 | NPK 0:0:51 | 0.5 |
Grafting of Scion
It is done from September-October. Irrigation is done 2 days before grafting to increase the sap flow. Optimum conditions to obtain successful grafts include a temperature of 300 -350C with Relative Humidity of 80%. Callose formation at the union followed by sprouting of bud after 10 days of grafting are signs of a successful graft.
Care of the Grape Plant After Grafting
- Irrigation – Light irrigation of plants must be done on daily basis for 1 month after grafting, thereafter irrigation can be done on alternate days for heavy soils and every day in light soil.
- Nutrient Management
| Manure and Fertilizer Applied to Plant After Grafting | ||
| Period After Grafting (in Days) | Nutrient/Fertilizer formulation | Quantity (kg/acre/day) |
| 0-15 | Urea | 0.5 |
| 16-30 | NPK 19:19:19 | 1.0 |
| 31-45 | Urea | 1.0 |
| 46-60 | NPK 19:19:19 | 1.0 |
| 61-75 | Urea | 1.0 |
| 76-90 | NPK 19:19:19 | 1.0 |
| 91-105 | NPK 13:0:46 | 1.0 |
| 106-120 | NPK 0:0:51 | 1.0 |
Training Procedure of Grape Vines in Growing Grapes Organically
Vineyards can be trained in a variety of ways based on the vigour of cultivar and location. Pergola and vertical trellis are extensively used methods of training in China while Japan uses the horizontal trellis method of training. In India, the most popular methods of training are Bower, Telephone, and Flat Roof Gable systems.
Pruning Procedure of Grape Vines in Growing Grapes Organically
- Backward Pruning: It is done after the harvests in this 1-2 basal buds are retained while the rest are pruned. These buds sprout to form shoots that reserve food. It is also called foundation pruning.
- Forward Pruning: It is done during the month of September-October. These shoots are called canes at maturity, the pruning is done after the 5th basal bud for table purpose grapes and 3rd-4th basal bud for cultivars used for winemaking. It is also called fruit pruning
Nutrient Management in Growing Grapes Organically
The nutrient requirement of grapes is throughout the year. Grapes require potassium more than nitrogen and phosphorous is only required at the time of fruit bud formation. It is highly recommended that farmers follow fertigation technique to improve the nutrient use efficiency by the plants.
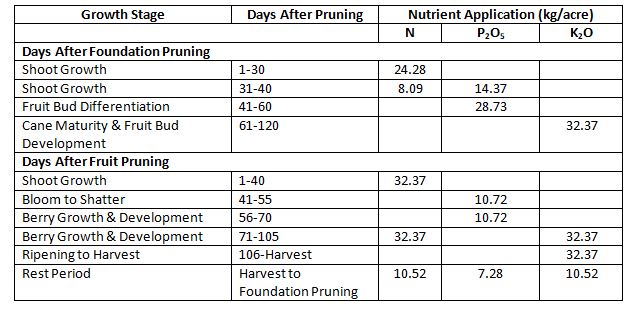
Irrigation Management in Growing Grapes Organically
The sub-surface irrigation/ drip irrigation method is best for grapes cultivation with high water use efficiency it also ensures adequate moisture availability in the root zone. The irrigation water must be checked before irrigation for EC, pH, and SAR as the plants are sensitive to alkaline pH and high EC which can drastically reduce the yield. Irrigation scheduling for grapes can be done in the following way:
| Growth Stage | Water Requirement (in L/day/acre) |
| 1-40 days after backward pruning | 19425-24280 |
| 41-100 days after backward pruning | 9713-12950 |
| 101 days after backward pruning to forward pruning | 6070-8094 |
| 1-45 days after forwarding pruning | 8094-9713 |
| 46-75 days after forwarding pruning | 6475-8094 |
| 76-100 days after forwarding pruning | 19425-24280 |
| 101 days after forward pruning till harvesting | 14569-19425 |
| After harvesting until backward pruning | 8094-9713 |
Weed Management in Growing Grapes Organically
Cynodon dactylon and Cyperus rotundus are the most notorious weed in the grape vineyard. These weeds must be kept in check throughout the year. Cultural practices must be followed for the eradication of weed. Hand-picking and deep ploughing of fields in summer are effective to some extent. While in organic cultivation mulching of field with 3” thick Baggase @ 10 tonnes per acre also helped in controlling the weed. Green manure crops can also be intercropped in the rainy season and at the time of flowering, they should be ploughed. It is advantageous to control weed as well as providing organic manure to the soil.
Disease Management in Growing Grapes Organically
Powdery Mildew and Downy Mildew are the major diseases responsible for loss of harvest throughout Asia. Some other diseases are Anthracnose, Bacterial Blight, and Rust.
- Powdery Mildew – Major symptom of the disease I the development of greyish-white growth on leaves and berries.
- Downy Mildew – Lower leaf surface is covered by milky white mycelium and pale-olive spots appear on flowers and berries are the characteristic symptoms of the disease.
- Anthracnose – This disease affects tender aerial parts of the plant characterized by dark brown sunken spots. It majorly affects the leaf.
- Bacterial Blight – the symptoms of this disease include water-soaked black spots on leaves and elliptical lesions on young canes.
- Rust – The lower surface of leaf pale yellow pustules of uredospores while upper surface shows characteristic pin-head lesion.
Management of the above-mentioned disease through eco-friendly chemicals and bio-control agents is still under research and no proven technique has still been discovered to counter the loss, though we can avoid the losses by eradicating disease-infected shoots before they spread to the vineyard. The maintenance of Phyto-sanitation plays an important role in controlling the spread of disease and thus reducing the losses. A high dose of nitrogen is also conducive to disease development hence quantification of fertilizer is an important step. Spraying of NSKE at fortnightly intervals might be beneficial to avoid the disease while in case of heave infection spray must be done at 4-5 days intervals.
Pest Management in Growing Grapes Organically
The major pests of the grape vineyard are Mealy Bugs, Thrips, Chaffer Bettle and Bees & Wasps.
- Mealy Bugs – Among these Pink Mealy Bugs majorly infest grape vineyards. The caused damage by sucking the plant sap from tender parts which lead to curling and malformation of wine parts. The occurrence is recorded majorly after fruit pruning. For controlling mealybugs spray of soap solution with 5ml of NSKE in 11-liter water is effective to some extent. But following the day of NSKE spray, the plants must be sprayed by water to avoid flaking on leaves.
- Thrips – these are sucking pests. Both nymphs and adults suck sap from foliage and flowers leading to curling and cupping of young leaves. They cause a heavy loss in yield as they suck sap from the ovaries of the flower during the berry setting stage which leads to flower shedding. Management can be done by as mentioned in the mealybugs.
- Chaffer Beetles – These insects are leaf eaters and cause heavy defoliation of plants leading to very low or no yield. They can be effectively managed by the installation of light traps. The traps should be installed 15 feet away from the vineyard and 3 feet above the ground.
- Bees & Wasps – They cause damage by puncturing the ripe fruits and feeding on them. Honeybees are also attracted to punctured fruits. This damage can be controlled by burning any arboreal nest or beehive lying in the vicinity of the vineyard and covering the berry bunch with cloth bags.
After berry formation, bagging is one of the effective ways of controlling pest damage.
Harvesting of Grapes
Grapes are non-climacteric fruit. Thus, it must be harvested after ripening. Maturity indices for Grapes fixed by AGMARK are a minimum of 160Brix TSS and a Sugar Acid ratio of 20. Harvesting should be done by a skilled person by using sharp scissors/blades to detach the bunch from the parent plant without causing any injury to either of them. Harvesting must be done in the morning hours before berry temperature rises. After harvest, the berries must be kept in shade for4-6 hours for pre-cooling and lowering the berry temperature.
The yield of Grapes
You may also check this: Growing Noni Fruit.

The yield of grapes varies with the type of variety cultivated in general it is about 6-10 tonnes per acre when following organic practices of agriculture for grapes production.
- Crops Grown in Summer Season: Best Choices for Summer Gardening
- Organic Pest Control for Tomato Farming
- How to Maximize Sheep Farming Profit
- Broccoli Varieties: Choosing the Right Cultivars for Your Farm
- How to Raise Pigs in Your Own Backyard: A Comprehensive Guide
- Budget Friendly Sheep Shed Ideas: Cheap and Low-Cost Tips
- How Much Do Cattle Farmers Make: Revenue Streams in Cattle Farming
- Management Pests and Diseases in Your Cotton Field
- Sheep Farming Business Plan for Beginners
- Aquaponic Farming at Home: A Step-By-Step Guide
- Profitable Village Farming Business Ideas in 2024
- High-Yield Aquaculture: Fast-Growing Fish for Farming
- Effective Fish Pond Construction Techniques for Beginners
- Irrigation and Water Management in Pineapple Farming
- Blossom to Harvest: Mastering Flowering and Pollination in Papaya Farming
- Pig Fattening Essentials: From Selection to Sale for Beginners
- Raising Wagyu Cattle: A Complete Guide for Premium Beef Production
- Soil Types and Their Water Holding Capacity
- Optimizing Irrigation Schedules for Coconut Groves for Enhanced Yield
- Espresso Your Garden: Coffee Grounds for Healthier Acid-Loving Plants
- The Best Soil Mix for Snake Plants: How to Mix Your Own Snake Plant Soil
- Green Thumb Success: Expert Tips for Cultivating Greenhouse Beans All Year Round
- Bloom All Year Round: The Ultimate Guide to Indoor Hyacinth Care
- Eco-Friendly Gardening: How to Make Liquid Fertilizer from Kitchen Waste
